Flow Simulation in Medical and Safety Technology
Many projects from this area were made in cooperation with the Dräger AG, Lübeck. There are questions for which the usage of flow simulation tools is reasonable. Development phases can be shortened and costs reduced because expensive prototypes can be simplified or even dropped, and parameter studies can be accomplished without a large effort.
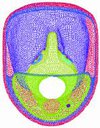

As an example, we will take a closer look on the flow calculation for a respiratory mask. During the usage of such a mask, it is possible that the sight glass becomes steamy. This effect always happens when the air comes in touch with a surface which is colder than the saturation temperature - in the case of the mask, for example, through a cold visor and a high humidity inside the mask.
The misting of the glass can be prevented or reduced when the dry and unsaturated air from the inhalation is used to rinse the glass. We try to obtain the best possible incident flow towards the glass by using a flow simulation. On the basis of a 3D CAD geometry of the mask, a model for the flow simulation is developed: see figure on the left.
With this, it is possible to create a CFD analysis from complex geometry in a short time. In addition, the effects of changes can be tested directly on the model. Also new parts can be added to the model. In the case of the mask, the actual condition while inhaling is examined at first.
After that, the flow behaviour is tested by adding different components and rated by the optimal rinsing of the glass.
Another example is the humidification of dry ventilation air through steam. During machine ventilation of patients, the dry and cold air is warmed and moistened by the respiratory humidifier. This happens by mixing hot steam and ventilation air. With the help of a simulation, you can see how thermodynamics of the evaporator process, the flow in the mixing chamber and the heat conduction react when using an alternative heating of the evaporation pipe (see: Paper).
With the help of flow simulation, you can also calculate flows in connection to heat and mass exchange processes. Furthermore, it is possible to simulate the behaviour of free surface flows.
Selected reports
(full list here)
- Untersuchungen der transsonischen Durchströmung eines Ejektors
M. Schrumpf, P. Schaffarczyk
Bericht des Labors für numerische Mechanik 21, Kiel, Feb. 2001 - Erarbeitung, Simulation und Bewertung von Lösungsvarianten zur Vermeidung des Beschlagens der Sichtscheibe der HPS-Atemschutzmaske ohne Verwendung von Steuerventilen durch gezielte Umlenkung
M. Schrumpf, P. Schaffarczyk
Bericht des Labors für numerische Mechanik 20, Kiel, November 2000 - Numerical Investigations of Heat Exchange of dry Air with Overheated Steam.
M. Schrumpf, P. Schaffarczyk, J. Koch
FLUENT Anwendertreffen 2000, Bingen, 18/19 Sept. 2000 - Numerische Untersuchungen zu den Wärmetauschvorgängen bei der Anfeuchtung trockener Beatmungsluft durch Dampf
M. Schrumpf, P. Schaffarczyk
Bericht des Labors für numerische Mechanik 18, Kiel, April 2000 - Vergleich von Kegeln und Sieben als Strömungsvergleichmäßiger in einem Durchflußsensor einschließlich y-förmigen Anschlußstück zum Beatmungsgerät
M. Schrumpf, P. Schaffarczyk
Bericht des Labors für numerische Mechanik 17, Kiel, Oktober 1999 - Analyse strömungshomogenisierender Einbauten in Durchflußsensoren für Beatmungsgeräte
M. Schrumpf, P. Schaffarczyk
Bericht des Labors für numerische Mechanik 16, Kiel, April 1999
